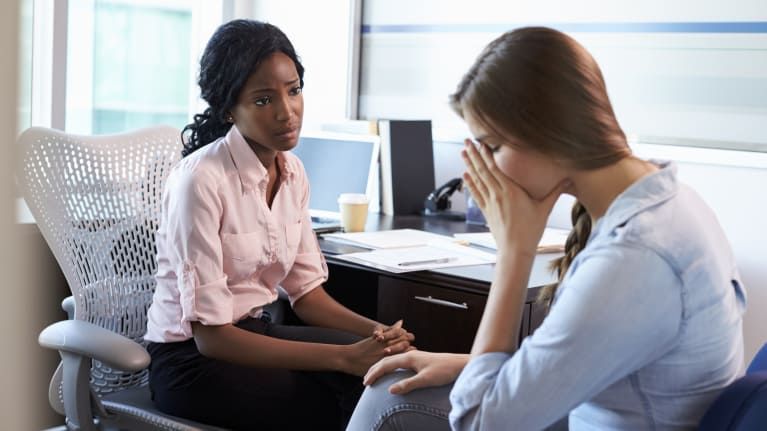
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace
Section 354 of the Indian Penal code stipulates what comprises Sexual Harassment. The Sexual Harassment of Women At Workplace Act is a legislative Act in India that strives to protect women from sexual harassment at their workplace. It provides various provisions and punishments with regard to different ways in which women are harassed in their workplaces.
 .
.
Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace ACT, 2013
FOLLOWING ARE SOME OF THE IMPORTANT FEATURES OF THE ACT :
The Act defines sexual harassment at the workplace and creates a mechanism for redressal of complaints. It also provides safeguards against false or malicious charges.
WHO IS AN AGGRIEVED WOMAN?
The definition of “aggrieved woman”, who will get protection under the Act is extremely wide to cover all women, irrespective of her age or employment status, whether in the organized or unorganized sectors, public or private, and covers clients, customers, and domestic workers as well
WHO IS AN EMPLOYER?
An employer has been defined as any person who is responsible for management, supervision, and control of the workplace and includes persons who formulate and administer policies of such an organization under Section 2(g)
COMPLAINTS COMMITTEE :
The Act makes it necessary to establish ICC (Internal Complaints Committee) and LCC (Local Complaints Committee) to redress women working in the unorganized sector or small establishments.
Every employer is required to constitute an Internal Complaints Committee at each office or branch with 10 or more employees. The District Officer is required to constitute a Local Complaints Committee at each district, and if required at the block level.
The Committee is required to complete the inquiry within a time period of 90 days. On completion of the inquiry, the report will be sent to the employer or the District Officer, as the case may be, they are mandated to take action on the report within 60 days
The Complaints Committees have the powers of civil courts for gathering evidence.
The Complaints Committees are required to provide for conciliation before initiating an inquiry if requested by the complainant.
OTHER IMPORTANT PROVISIONS
The inquiry process under the Act should be confidential and the Act lays down a penalty of Rs 5000 on the person who has breached confidentiality.
The Act requires employers to conduct education and sensitization programs and develop policies against sexual harassment, among other obligations.
Penalties have been prescribed for employers. Non-compliance with the provisions of the Act shall be punishable with a fine of up to ₹ 50,000. Repeated violations may lead to higher penalties and cancellation of license or registration to conduct business.
The government can order an officer to inspect workplace and records related to sexual harassment in any organization.
Read the Handbook on Sexual Harassment of women at Workplace by the Ministry of Child and Women Development, Government of India.